What is 5G RedCap?
Introduction to 5G RedCap
This article explores the technical foundations, advantages, and real-world applications of 5G RedCap. Whether you’re looking to enhance industrial processes, deploy cost-effective IoT solutions, or future-proof your connectivity strategy, this guide will provide valuable insights into how 5G RedCap can meet your needs.
Table of contents
- Technical foundations of 5G RedCap
- Key Features and benefits of 5G RedCap
- Real-world applications of 5G RedCap devices
- Use Cases of 5G RedCap
- Strategic Considerations for Businesses
- Reliability and Security of 5G RedCap
- 5G RedCap product selection
- Summary
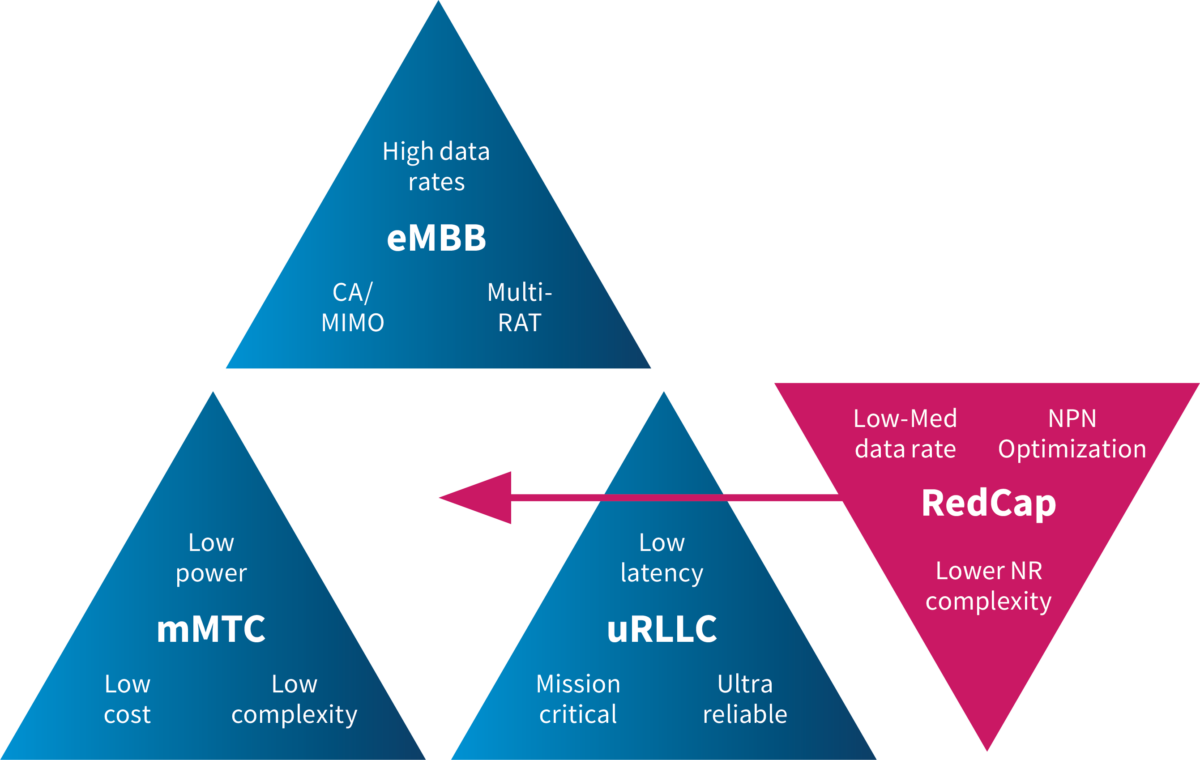
5G RedCap (Reduced Capability), also known as NR-Light, is a streamlined version of 5G technology designed for devices and applications that don’t require the full power of traditional 5G. While standard 5G delivers ultra-fast speeds and massive connectivity for high-performance applications, RedCap optimises connectivity for IoT, industrial automation, and wearable technology, where simpler, cost-effective solutions are more practical.
The core concept is to streamline certain functionalities, reducing hardware costs and minimising energy consumption while still leveraging the key advantages of 5G networks—such as low latency and the ability to support a high number of connected devices. "Connection density" refers to the number of devices or links that can operate simultaneously within a given network or geographic area.

While 4G was primarily designed for data-intensive applications, 5G expands its focus beyond high data rates to support a vast number of devices with diverse performance needs. 5G RedCap bridges this gap by offering a cost-effective and resource-efficient solution—perfect for applications where reliability and efficiency take priority over peak data speeds.
The biggest advantage of 5G RedCap is its balance of performance, cost-efficiency, and power consumption. By reducing complexity in device design and connectivity requirements, RedCap provides a scalable solution that maximises reliability while keeping costs low. With increasing adoption across industries such as smart cities, industrial IoT (IIoT), healthcare, and logistics, this technology is set to play a key role in shaping the future of wireless communication.
Technical foundations of 5G RedCap
Streamlined 5G NR: RedCap’s architecture for efficient industrial and IoT deployment
5G RedCap is built on the same foundation as 5G New Radio (NR) but with key modifications to reduce complexity and cost. The technical architecture of 5G RedCap differs fundamentally from conventional 5G NR (New Radio) solutions. In RedCap, certain functionalities as well as antenna configurations are deliberately reduced to lower complexity:
-
One of the main differences is its narrower frequency band operation. RedCap devices typically use a 20 MHz bandwidth, making them more efficient for low-data applications while remaining compatible with broader 5G networks.
-
Another major refinement is the modulation scheme. While LTE Cat4 typically employs 64 QAM in the downlink and 16 QAM in the uplink – enabling a more robust yet lower data throughput – RedCap supports 256 QAM. This higher-order modulation increases spectral efficiency, allowing transmission of 8 bits per symbol within the available spectrum while maintaining reliability. This results in significantly higher spectral efficiency, making it possible to transmit more data within a 20 MHz channel, provided that the signal quality is sufficiently high.
-
RedCap also simplifies antenna configurations. Traditional 5G deployments use extensive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) setups with multiple antennas to boost speeds, but RedCap takes a different approach. Most RedCap devices use 1×1 or 2×2 MIMO, prioritising signal stability over peak speeds. This reduces hardware costs and improves energy efficiency—a crucial factor for IoT devices that need long battery life or devices deployed in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
Key Features and benefits of 5G RedCap
Why 5G RedCap is the smart choice for future-ready industrial and IoT solutions
-
Cost-effective bandwidth
Unlike full 5G, which is designed for high-speed applications, RedCap delivers just the right amount of bandwidth needed for IoT and industrial use cases. This reduces network congestion and enhances operational efficiency without unnecessary costs. This approach is aimed at matching data transfer to the actual need, which is particularly advantageous for applications with moderate data rates. -
Energy efficiency
One of the biggest advantages of 5G RedCap is its low power consumption. Optimised protocols, lean communication processes, and simplified signal processing extend battery life for IoT devices and wearables, reducing maintenance costs and ensuring long-term reliability. -
Compact, simplified hardware
With fewer antennas and less complex hardware requirements, RedCap devices are smaller and easier to integrate into smart sensors, industrial monitoring systems, and consumer wearables. This leads to more practical and cost-efficient deployments.
-
Optimised software for stability and efficiency
Beyond hardware improvements, 5G RedCap also benefits from software optimisations. Tailored protocols and streamlined communication procedures ensure that even resource-limited devices maintain a stable and reliable connection. -
Seamless network integration
5G RedCap is designed to work within existing 5G infrastructures, meaning businesses can adopt it without major network upgrades. This makes deployment cost-effective and ensures future-proof connectivity. -
Future-proofing IoT solutions
Many industries require connectivity solutions with long product life cycles (10 years or more). With LTE networks gradually being phased out, RedCap offers a sustainable, forward-compatible solution for IoT applications needing low to moderate data rates without requiring full 5G capabilities.
Real-world applications of 5G RedCap devices
The market for 5G RedCap devices is experiencing significant growth, as manufacturers increasingly recognise the need to create devices tailored to the specific requirements of IoT applications. While adopting RedCap may not always be technically necessary at present, customers often demand 5G support for products with long lifecycles (10+ years) to ensure their long-term viability. Currently, the first series of production-ready products are being launched.
From a design standpoint, several challenges must be addressed: devices need to be durable and energy-efficient to operate reliably across a range of environments. Cost optimisation is crucial, as the target market frequently involves price-sensitive applications. In addition to technical requirements, strict certification and compliance standards must be met to ensure smooth integration into existing 5G networks.
Manufacturers work closely with regulatory bodies to guarantee that devices comply with both current and future standards. This ongoing development is driven by continuous innovation that affects not just hardware but also the supporting software solutions. Regular updates and improvements are essential to meeting the ever-evolving demands of the market.
Use Cases of 5G RedCap
The applications of 5G RedCap are diverse and offer significant benefits across various industries
These varied use cases demonstrate that 5G RedCap is not meant to replace full 5G solutions but to complement them in scenarios that demand efficiency and cost optimisation.
Strategic Considerations for Businesses
The economic and organisational impacts of 5G RedCap are multifaceted, presenting both challenges and opportunities for businesses.
Companies must adapt their existing business models to align with the new technological landscape while capitalising on emerging opportunities.
-
Financial considerations
Implementing RedCap solutions results in significant cost reductions compared to full-scale 5G. Lower hardware costs and reduced energy consumption offer an attractive cost-benefit ratio. A comprehensive ROI analysis shows that industries with low-data applications and high-volume units stand to benefit the most from this technology. -
Administrative challenges
The introduction of new device types typically requires a review and update of internal policies and processes. Companies need to develop new strategies for device management, data security, and regulatory compliance. This includes training employees and adjusting IT infrastructures to ensure smooth operations. However, when transitioning to 5G technology, these impacts tend to be minimal to negligible.
-
Organisational impact
Specialised teams may be needed for planning, implementation, and maintenance of the new systems. Yet, these efforts are comparable to those required for other technologies and are relatively low for 5G RedCap. -
Competitive analysis and market dynamics
Since RedCap is still a very young technology, early involvement offers strategic advantages. Investing in RedCap now can provide long-term opportunities and safeguard future investments. -
Opportunities and Partnerships
Collaboration between technology providers and industrial customers is key. By forming targeted partnerships, businesses can develop innovative solutions tailored to the needs of specific industries, fostering synergies that enhance both technological and economic competitiveness.
Reliability and Security of 5G RedCap
When implementing 5G RedCap, two key aspects are paramount: network stability and protection against cyber threats.
-
Reliability
For use in critical applications such as medical monitoring or smart grids, 5G RedCap must provide reliable performance, even in challenging environments. Achieving this requires not only robust hardware but also optimised software solutions that can detect and address disturbances early. Testing across various scenarios has demonstrated that 5G RedCap can maintain a stable connection, even under difficult conditions, which is vital for time-sensitive applications. -
Security considerations
Although 5G RedCap is designed with reduced complexity, security remains a top priority. Regular firmware updates and patches are essential for closing newly discovered vulnerabilities. Compared to 4G, which offers strong security protocols but is not always optimised for devices with limited processing capabilities, 5G RedCap incorporates advanced encryption methods and authentication processes. Additionally, the 5G architecture enables network slicing, allowing the creation of isolated security zones for more targeted monitoring and control. These features significantly enhance protection against cyberattacks, providing a crucial advantage in industries such as industrial manufacturing and healthcare, where security breaches could have serious consequences.
-
Industrial and operational integration
5G RedCap functions as a transparent communication technology for the end user, meaning its integration into existing systems does not require a complete redesign of hardware. Existing devices can typically remain in use, with the primary changes occurring in the network infrastructure, configuration, and management. -
Industrial applications
In industries such as production and manufacturing, real-time monitoring is essential. Private 5G networks allow sensors and automation systems to be seamlessly integrated into existing setups, providing stable, low-latency connections. Case studies show that adopting 5G not only enhances production quality but also significantly reduces downtime. -
Process optimisation
Rather than completely redesigning the rollout process, 5G RedCap allows for seamless integration into existing network infrastructures. This means that the setup and commissioning of RedCap networks can largely follow familiar procedures. Best practices include the gradual integration of new components, adapting existing interfaces, and continuously monitoring system performance. This approach ensures a smooth transition to the new technology without disrupting ongoing operations. Additionally, the introduction of 5G solutions opens up opportunities to rethink and optimise traditional business processes. For example, real-time machine connectivity can improve material flow management and help identify bottlenecks early, leading to increased efficiency and cost reductions over the long term.
Research and technological developments
Recent studies indicate that 5G RedCap modules , such as the EM8695 , can reduce energy consumption by up to 65% compared to LTE Cat-4, while achieving data rates of up to 223 Mbps on the downlink and 123 Mbps on the uplink.
These quantitative results prove that RedCap offers an efficient and cost-effective alternative in real world IoT scenarios. However, research gaps remain: further studies are required to refine network slicing strategies to ensure smooth interaction between RedCap and existing LTE fallback solutions. Additionally, the performance of RedCap in dense IoT environments, particularly under real-world interference conditions, needs further exploration, along with potential measures to enhance its performance.
On the technology front, innovations in chipsets and antenna designs are advancing RedCap’s efficiency. Modern 5G RedCap modules feature simplified antenna configurations and advanced power-saving mechanisms like eDRX, which help extend battery life in portable devices. Looking ahead, additional optimisations are expected with 3GPP Release 18, including the introduction of eRedCap, which may lower the minimum data rate to 10 Mbps, enabling even more cost-effective IoT applications.
5G RedCap modules and routers for scalable IoT and industrial connectivity
Overview of our 5G RedCap modules and routers
Challenges and Considerations
Deploying 5G RedCap presents unique challenges beyond standard security measures. While RedCap devices have a reduced attack surface due to their simplified architecture, maintaining robust security remains essential. Regular updates and well-defined security protocols are necessary to promptly address potential vulnerabilities.
Interference is another key consideration, particularly in densely populated IoT environments. Effective solutions include adaptive frequency management algorithms and enhanced filtering techniques to minimise disruptions from adjacent channels. These optimisations operate seamlessly in the background, ensuring a smooth user experience without requiring direct intervention.
Future Prospects and Developments
The current 3GPP Standard Release 17 is just a stepping stone, with Release 18 and enhanced RedCap (eRedCap) already finalised, paving the way for new modules and devices. Unlike typical technological advancements that focus on increasing data rates, Release 18 takes a different approach by reducing them—improving energy efficiency and aligning RedCap more closely with massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC) use cases. This makes it an ideal solution for sensors, battery-powered devices, and low-bandwidth applications currently relying on LTE Cat 1, Cat 1-bis, or LTE-M.
With the high demand for these applications, the adoption of (e)RedCap is expected to accelerate rapidly. This evolution will cement RedCap’s role in the future IoT landscape, opening new opportunities for engineers to develop innovative solutions that further drive progress in the field.
Conclusion
5G RedCap plays a crucial role in the 5G ecosystem, providing a tailored solution for IoT applications that do not require full 5G capabilities. By eliminating non-essential features, it reduces costs and energy consumption, ensuring long-term network viability. Ongoing research and development highlight RedCap’s significant potential, making it a valuable opportunity for engineers and businesses to future-proof their systems and maximise its benefits.
5G RedCap is more than just a scaled-down version of 5G—it is a purpose-built solution that optimises connectivity for industries requiring efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. By adopting this technology, businesses can unlock new opportunities, streamline operations, and prepare for the future of connected ecosystems.